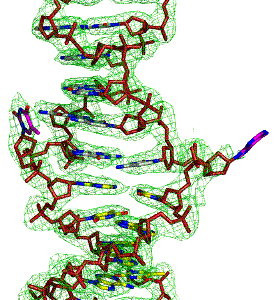
X-ray Crystallography
X-ray crystallography is a structural biology technique that determines the atomic arrangement of molecules by analyzing the diffraction patterns produced when X-rays pass through protein crystals. It offers exceptionally high-resolution structural information, making it a gold-standard method for studying well-ordered biomolecules. This technique enables precise visualization of active sites, ligand-binding pockets, and subtle conformational details. We applied X-ray crystallography to elucidate DNA-protein–ligand interactions with atomic precision.
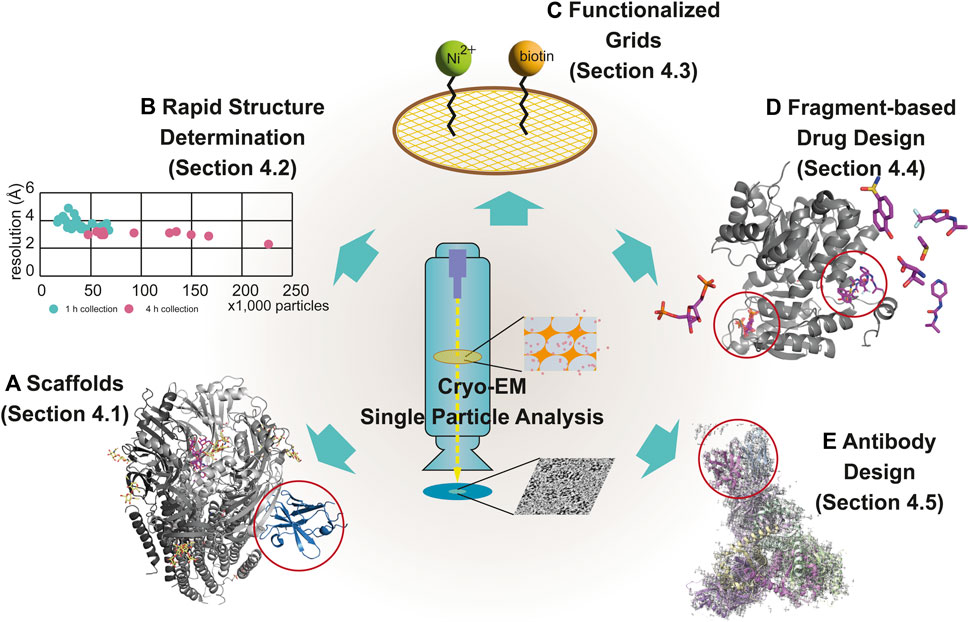
Cryo-Electron Microscopy
Cryo-electron microscopy is an imaging method that captures biomolecules in near-native, vitrified states using electron beams, without requiring crystallization. Its key strength lies in visualizing large, flexible, or complex assemblies that are difficult to crystallize, and recent technological advances allow near-atomic resolution for many systems. We are applying CryoEM to study dynamic of macromolecular complexes and membrane proteins.
Technical developments
in Cryo-EM
We are developing advanced techniques and methodologies to overcome current challenges in cryo-EM sample preparation. In addition, we are establishing new approaches to apply cryo-EM in chemical screening and in the structural determination of challenging targets, such as low–molecular-weight proteins.
Recent Publications
1. Lee, J., Kim, T. and Kim, K.K., 2025. Optimizing Sample Preparation for Cryogenic Electron Microscopy. Journal of Visualized Experiments (JoVE), (218), p.e67237.
2. Cebi, E., Lee, J., Subramani, V.K., Bak, N., Oh, C. and Kim, K.K., 2024. Cryo-electron microscopy-based drug design. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, 11, p.1342179.Lee, J., Ryu, B., Kim, T. and Kim, K.K., 2024.
3. Cryo-EM structure of a 16.5-kDa small heat-shock protein from Methanocaldococcus jannaschii. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 258, p.128763.
4. Le, K., Kannappan, S., Kim, T., Lee, J.H., Lee, H.R. and Kim, K.K., 2023. Structural understanding of SARS-CoV-2 virus entry to host cells. frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, 10, p.1288686.
5. Oh, C., Kim, T.D. and Kim, K.K., 2019. Carboxylic ester hydrolases in bacteria: Active site, structure, function and application. Crystals, 9(11), p.597.
6. Kim, D., Hur, J., Han, J.H., Ha, S.C., Shin, D., Lee, S., Park, S., Sugiyama, H. and Kim, K.K., 2018. Sequence preference and structural heterogeneity of BZ junctions. Nucleic acids research, 46(19), pp.10504-10513.
7. Oh, C., Ryu, B.H., Yoo, W., Nguyen, D.D., Kim, T., Ha, S.C., Kim, T.D. and Kim, K.K., 2018. Identification and crystallographic analysis of a new carbohydrate acetylesterase (SmAcE1) from Sinorhizobium meliloti. Crystals, 8(1), p.12.
8. Ngo, T.D., Oh, C., Mizar, P., Baek, M., Park, K.S., Nguyen, L., Byeon, H., Yoon, S., Ryu, Y., Ryu, B.H. and Kim, T.D., 2018. Structural basis for the enantioselectivity of esterase Est-Y29 toward (S)-ketoprofen. ACS Catalysis, 9(1), pp.755-767.