The Cell Fate Manipulation group explores how adult stem cells and somatic cells can be guided toward specific fates for regenerative medicine. Our research spans somatic cell reprogramming, stem cell priming, and cellular rejuvenation, using biologics such as exosomes, non-coding RNAs, and small molecules in both in vitro and in vivo set ups. We also employ bioinformatics tools to study the cell-specific gene regulatory networks and identify key molecular targets to control cell identity and function.
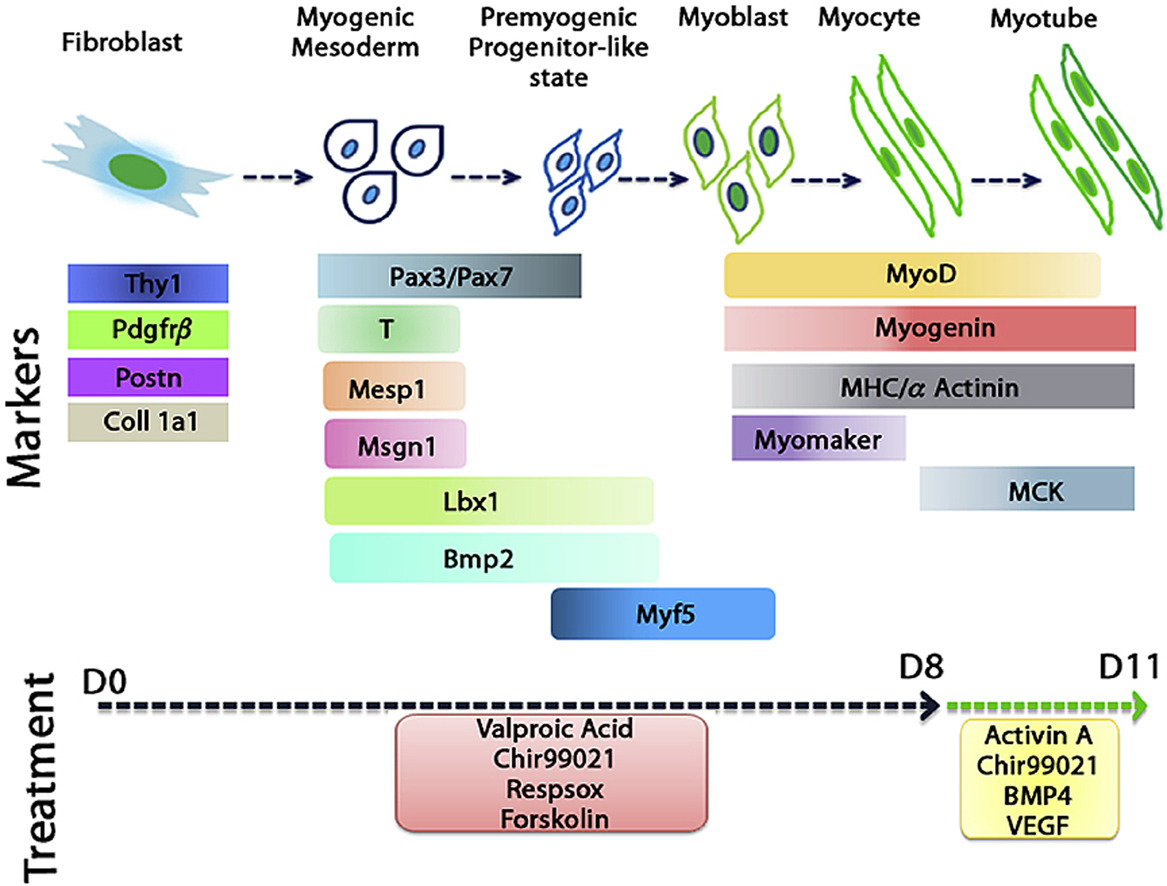
We have developed direct reprogramming strategies bypassing the pluripotent state to generate therapeutically relevant cell types, including neurons, pancreatic beta cells, cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and adipocytes. Our work also examines how immune and stromal cell components within the tumour microenvironment can be targeted to reduce tumor burden and metastasis. To increase the precision and efficiency of reprogramming, we are working on the development of advanced delivery systems such as neosomes, nanoparticles, and microneedle platforms.
In parallel, we are building in vitro models of cellular aging to study age-associated changes and develop interventions that restore youthful function. Through integrated transcriptomic and epigenetic approaches, we aim to uncover molecular targets for cellular rejuvenation and improvement of the regenerative abilities of aging cells.
Recent Publications
1. Kannappan, S., Kim, Y., De, D., Ginting, R.P., Yang, H.G., Kim, K., Bansal, V., Jung, S.M., Ahn, J.Y., Um, S.H. and Lee, M.W., 2025. In vivo brown adipogenic reprogramming induced by a small molecule cocktail. Biomaterials, p.123463.
2. Fernandes, G.S., Singh, R.D., De, D. and Kim, K.K., 2023. Strategic application of epigenetic regulators for efficient neuronal reprogramming of human fibroblasts. International journal of stem cells, 16(2), pp.156-167.
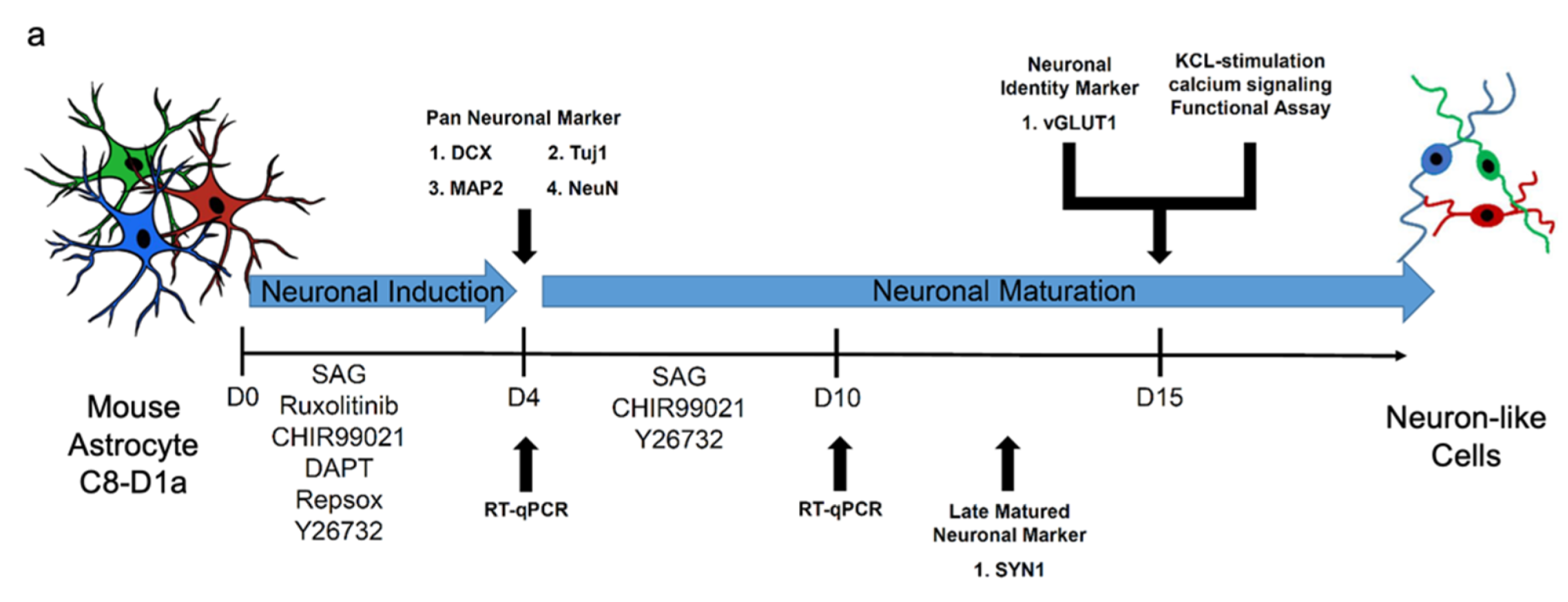
3. Fernandes, G.S., Singh, R.D. and Kim, K.K., 2022. Generation of a pure culture of neuron-like cells with a glutamatergic phenotype from mouse astrocytes. Biomedicines, 10(4), p.928.
4. Mandal, P., De, D., Im, D.U., Um, S.H. and Kim, K.K., 2020. Exosome-mediated differentiation of mouse embryonic fibroblasts and exocrine cells into β-like cells and the identification of key miRNAs for differentiation. Biomedicines, 8(11), p.485.
5. Lee, J.A., An, J., Taniguchi, J., Kashiwazaki, G., Pandian, G.N., Parveen, N., Kang, T.M., Sugiyama, H., De, D. and Kim, K.K., 2021. Targeted epigenetic modulation using a DNA‐based histone deacetylase inhibitor enhances cardiomyogenesis in mouse embryonic stem cells. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 236(5), pp.3946-3962.
6. Mandal, P., De, D., Yun, K. and Kim, K.K., 2020. Improved differentiation of human adipose stem cells to insulin-producing β-like cells using PDFGR kinase inhibitor Tyrphostin9. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 533(1), pp.132-138.